It Was All A Mirage: 2.5 Million Native-Born US Workers Were Just Revised Away
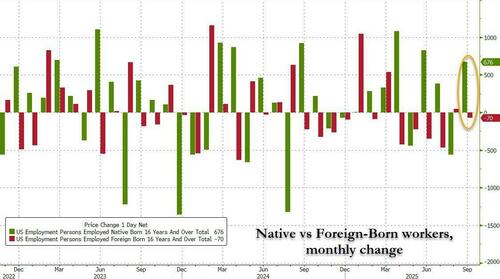
One of Donald Trump's core pre-election promises (along with cracking down on immigration and no more foreign wars) was to boost employment for local-born Americans at the expense of the record employment for foreign-born, mostly illegal, workers. And for a while it worked: four months ago, when discussing the September jobs report, we said that while the broader report was generally mixed, it was "indisputably strong when it comes to one thing: the rotation from foreign born workers to domestic ones. To wit: in September, the number of native-born workers surged by 676K (after the August drop of 561K), while foreign-born workers dropped by 70K."
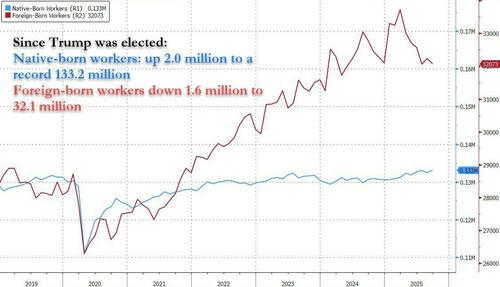
The data showed that since Trump entered the White House "the number of foreign born workers has slumped from a record 33.7 million in March 2025 to 32.1 million, a drop of $1.6 million. This has been offset by a slow but consistent increase in native-born workers which had been unchanged for six years since 2019 until the start of 2025, at which point it started to rise again, and has increased from 131.2 million in March 2025 to a new record high of 133.2 million in September."
Why does this matter? Because today's job report, which was undeniably dismal and sparked added to the sharp selloff across the market, also updated the working age population calculations to reflect the latest US Census population count for 2025. The new controls led to a big change in the January estimate of various employment metrics. They
- Lowered the working-age population by 231k;
- Reduced the labor force by 1,417k;
- Cut the employment level by around 1,432k;
- Lowered the labor-force participation rate by 0.46 percentage point and the employment-to-population ratio by 0.47 ppt.
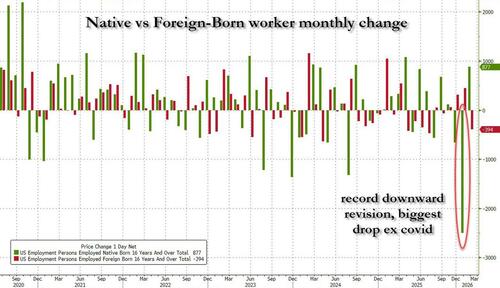
But perhaps the most important revision is that the entire boom in native-born employment was fake news: a statistical mirage spawned by some overzealous BLS staffer's excel model.
Presenting exhibit A: the monthly change in native and foreign-born workers. It shows that while the number of native-born workers in February did post a solid rise of 877K - using the revised data - this was only after the January data was revised comprehensively to wipe out a record 2.5 million (exactly) native born workers.
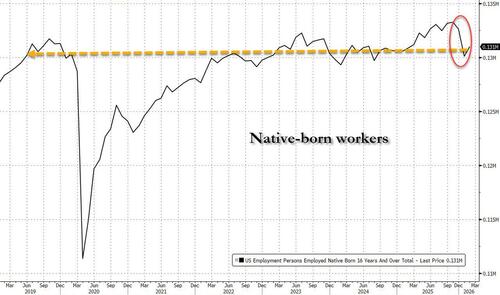
And here is what it looks like over the longer-term: at just under 131 million, the number of native born workers is back to where it was in 2019.
Which means that what some consider the greatest accomplishment of the Trump admin was nothing more than statistical fake news. The silver lining: at least there is the Iran war to keep everyone distracted.
Tyler Durden Fri, 03/06/2026 - 13:40


Recent comments